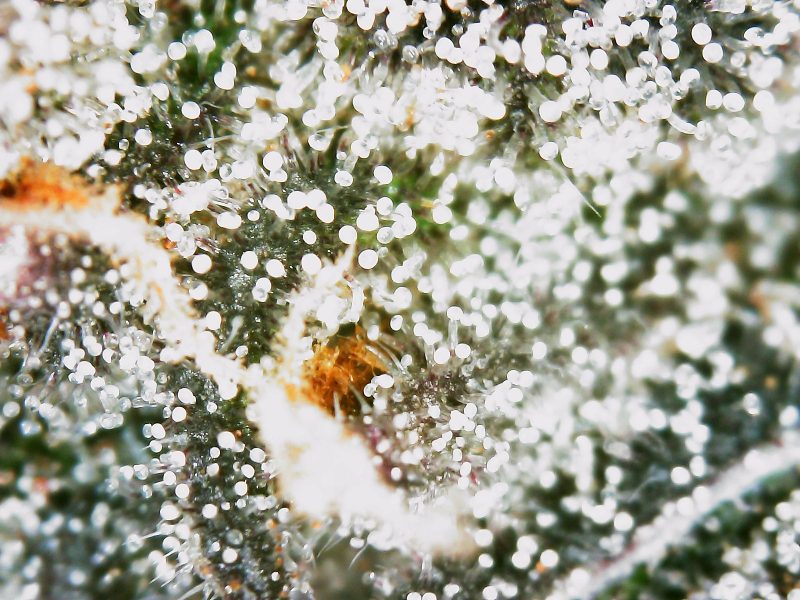
Unraveling the Science Behind Terpenes: The Aromatic Architects of Flavor
In the world of aromatics, terpenes are the unsung heroes that play a pivotal role in shaping the flavor profile of various substances, from the delightful notes in your morning cup of coffee to the complex bouquet of your favorite wine. These tiny molecules, found in the essential oils of plants, contribute significantly to the sensory experience of consuming natural products. But what exactly are terpenes, and how do they interact with our senses to create such an array of distinct flavors? Dive into the fascinating realm of terpene science to uncover the secrets behind their aromatic allure.
The Chemical Nature of Terpenes:
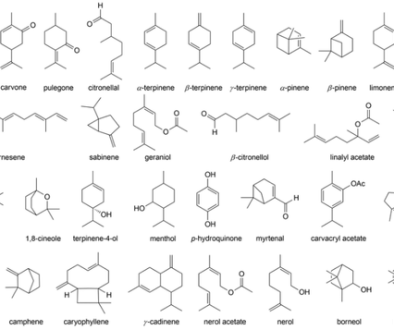
Terpenes are a large and diverse class of organic compounds produced by a wide variety of plants. They are the primary constituents of essential oils and are responsible for the fragrances of flowers, fruits, and herbs. These molecules are derived from isoprene units (C₅H8), which combine to form structures ranging from simple monoterpenes (two isoprene units) to complex diterpenes and triterpenes (four and six isoprene units, respectively). In total, over 40,000 different terpenes have been identified, each with its unique chemical makeup and sensory properties.
Terpenes and the Plant Kingdom:
In the plant world, terpenes serve multiple purposes. They act as protective agents, deterring predators and attracting pollinators. Their potent scents can also serve as a form of chemical communication between plants and other organisms. For instance, certain terpenes emitted by coniferous trees can alert nearby plants to the presence of herbivores, triggering a cascade of defensive responses. Moreover, these compounds contribute to the plant’s resin and latex production, which can act as a natural defense mechanism against pathogens and pests.
The Role of Terpenes in Flavor:
The human nose can detect a vast array of smells, thanks to the approximately 400 different types of olfactory receptors we possess. Terpenes interact with these receptors, allowing us to perceive an astonishing variety of aromas. The flavor profile of a plant is largely determined by the specific blend of terpenes it contains. For example, the terpene myrcene is responsible for the earthy, musky aroma found in hops, while limonene imparts a citrusy zest to lemons and limes.
In the context of food and beverages, terpenes are crucial for the overall taste experience. They interact with other compounds, such as flavonoids and cannabinoids, to produce a synergistic effect known as the entourage effect. This phenomenon enhances the perception of certain flavors and can also contribute to the medicinal properties of certain plants, like cannabis.
Terpenes in the Culinary World:
Chefs and mixologists are increasingly recognizing the power of terpenes to elevate the flavor profiles of their creations. By incorporating ingredients rich in specific terpenes, they can fine-tune the sensory experience of their dishes and drinks. For instance, basil contains high levels of linalool, which adds a floral, spicy note, while rosemary boasts camphene and pinene, contributing to its pine-like aroma. Understanding these interactions allows culinary professionals to create dishes that are not only delicious but also aromatically complex and satisfying.
The Science of Terpene Interactions:
The study of terpenes is complex, as their flavor potential is influenced by various factors, including concentration, temperature, and the presence of other compounds. Heat can alter terpene structures, leading to the evaporation of volatile molecules and the loss of certain flavor notes. This is why some chefs prefer to use raw herbs and spices to preserve the integrity of their terpene content.
Furthermore, the interactions between terpenes and other chemicals can either amplify or mask flavors. For example, the terpene beta-caryophyllene can enhance the spiciness of capsaicin, the compound responsible for the heat in chili peppers. Conversely, certain terpenes can interact to create entirely new flavor sensations, such as the minty coolness experienced when consuming a mint leaf alongside a citrus fruit, which is due to the combination of menthol in mint and limonene in the citrus.
Terpenes in the Cannabis Industry:
The cannabis plant is a veritable treasure trove of terpenes, boasting over 100 different types. These compounds are essential in determining the unique aroma and flavor of various cannabis strains, which can range from fruity and floral to diesel-like and piney. In addition to contributing to the overall sensory experience, terpenes are believed to play a significant role in the therapeutic effects of cannabis. Known as the “terpene-entourage effect,” they can modulate the activity of cannabinoids, such as THC and CBD, potentially increasing their medicinal benefits.
Researchers are actively studying the science of terpenes in cannabis to understand how these molecules interact with the human endocannabinoid system and influence the psychoactive and therapeutic effects of the plant. This knowledge is crucial for developing targeted cannabis products that can address specific health concerns while delivering a consistent and enjoyable user experience.
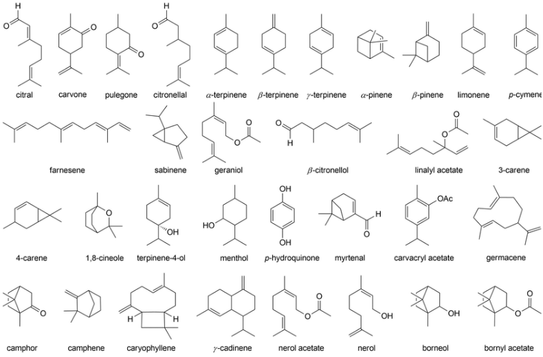
Terpenes are the aromatic building blocks that confer the diverse flavors and aromas found in nature. Their influence extends beyond our basic sensory experiences, playing a critical role in plant biology and even human health. As science continues to unravel the intricate web of terpene interactions, we can expect to see their use become more sophisticated in various industries, from food and beverage to aromatherapy and pharmaceuticals. Whether you’re a culinary enthusiast seeking to refine your palate or a cannabis connoisseur looking to understand the nuances of your favorite strain, the study of terpenes offers a fascinating window into the world of flavor and scent. So next time you savor the bouquet of a fine wine or the scent of a freshly peeled orange, remember the tiny molecules at work crafting these delightful sensations.